Introduction
The social determinants are a major factor in the formation of health outcomes, they influence everything from the access to healthcare to the presence of chronic diseases. In this guide, we will examine the various aspects of the impact of social determinants in health, thus, revealing the factors that have to do with the disparities and inequities of healthcare access and outcomes.
Defining Social Determinants in Health
What are Social Determinants?
Social determinants are the circumstances in which people are born, develop, live, work, and age. These factors cover a variety of life aspects which are socioeconomic status, education, employment, housing, social support networks, and access to healthcare services.
Understanding the Influence of Social Determinants
Social determinants are the major cause of health outcomes, they influence the individual and community well-being throughout life. They determine the way resources, opportunities, and power are distributed in society and hence, they are responsible for access to healthcare, quality of life, and overall health status.
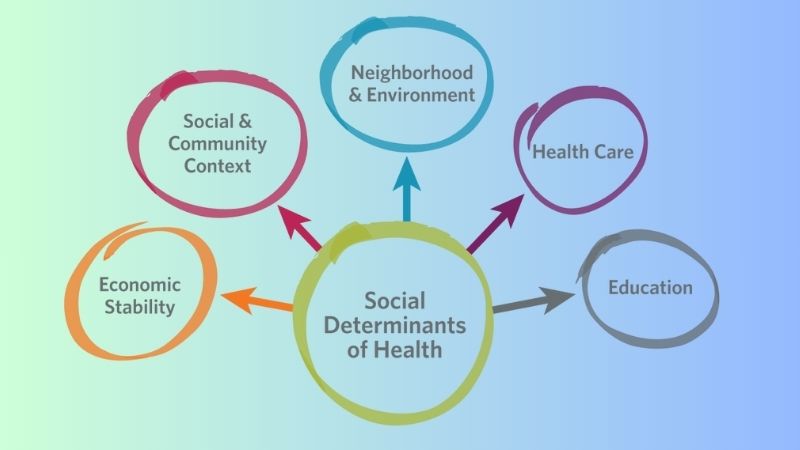
Key Social Determinants in Health and Their Impact
1. Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status, including income, education, and occupation, is one of the most significant predictors of health outcomes. Individuals with higher socioeconomic status tend to have better access to resources such as quality healthcare, nutritious food, safe housing, and education, which contribute to improved health outcomes.
2. Education
Education plays a crucial role in health, influencing factors such as health literacy, employment opportunities, income levels, and access to healthcare. Higher levels of education are associated with better health outcomes, as individuals with more education tend to make healthier lifestyle choices, have higher incomes, and access preventive healthcare services.
3. Environment
The physical and social environment in which people live can have a profound impact on health. Factors such as air and water quality, housing conditions, neighborhood safety, access to parks and recreational facilities, and community resources all influence health outcomes. Individuals living in disadvantaged environments may face increased exposure to environmental hazards, leading to higher rates of chronic diseases and health disparities.
4. Access to Healthcare
Access to healthcare services, including primary care, preventive care, specialty services, and medications, is a critical determinant of health. Barriers to healthcare access, such as lack of health insurance, transportation, language barriers, and cultural factors, can prevent individuals from receiving timely and appropriate care, leading to worse health outcomes and increased healthcare costs.
5. Social Support Networks
Social support networks, including family, friends, and community organizations, play a vital role in promoting health and well-being. Strong social connections provide emotional support, practical assistance, and a sense of belonging, buffering against the negative effects of stress and adversity. Conversely, social isolation and lack of social support are associated with poorer health outcomes and increased risk of mortality.
Addressing Health Inequities Through Action
1. Policy Interventions
Policies aimed at addressing social determinants in health can help reduce health inequities and improve outcomes for vulnerable populations. Examples include increasing access to affordable housing, expanding educational opportunities, implementing living wage policies, and investing in community development initiatives.
2. Healthcare System Reforms
Healthcare system reforms, such as expanding access to Medicaid, implementing telehealth services, and integrating social services into healthcare delivery, can help address disparities in healthcare access and outcomes. By adopting a holistic approach to health that addresses social, economic, and environmental factors, healthcare systems can better meet the needs of diverse populations.
3. Community Empowerment
Community-based approaches that empower individuals and communities to address social determinants in health can lead to sustainable improvements in health outcomes. Initiatives such as community health workers, peer support programs, and grassroots advocacy efforts can build capacity, foster collaboration, and promote health equity at the local level.
Conclusion
Social determinants in health play a profound role in shaping health outcomes and influencing access to resources, opportunities, and power within society. By addressing social determinants in health through policy interventions, healthcare system reforms, and community empowerment initiatives, we can work towards building a more equitable and inclusive healthcare system that promotes health and well-being for all.



