Introduction
The blockchain technology, in today’s fast-changing digital environment, is a real revolutionary tool. Such a pioneering invention has completely changed the course of ordinary paradigms toward everything from finance to healthcare and other sectors as well. Here, in the article, we will take a close look at the Blockchain topic covering its roles, uses, and the transformations that have already taken place due to it.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
What is Blockchain Technology?
In essence, Blockchain Technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that records transactions among multiple computers in a secure, immutable, and transparent way. In a blockchain, every block in the chain uniquely possesses a cryptographic hash of the previous block. Thus, every block is chained together, constructing a chain.
Types of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology keeps being improved, and there appear different types of blockchains accordingly. Here are some of the main types:
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are decentralized settings where everyone can join, see the transactions, and partake in the rules verification process. Taken in the illustration are Bitcoin and Ethereum. These blockchains present high transparency and security traits which, however, will probably lead to scalability and privacy constraints.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are permissioned networks with access and participation limited to owning the authorized entities only. For that reason, they are generally utilized by companies for their internal operations, plus they get more scalability and privacy in contrast to public blockchains. One of the examples can be Hyperledger Fabric and the Corda.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains can also be said to be a hybrid between public and private blockchains, in which a selected group of participants is allowed to control the consensus process. They are more centralized than private blockchains but with more limited access when compared to public ones. Consortium blockchains are common in the industry when several organizations such as supply chain management and finance require collaboration.
Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains are a merger of public and private blockchains. So, that they can take advantage of the beneficial features of each. Say for instance the hybrid blockchain that uses public blockchain for transparency and immutability, and private blockchain for scalability and data privacy.
Permissioned Blockchains
Differing from public blockchains, decentralized permissioned blockchains are characterized by the requirement of getting approval from the central authority to join the network or perform certain activities. This approach enables greater control within the network and in highly regulated industries where compliance is crucial.
Permissionless Blockchains
Permissionless blockchains, a generic term for public blockchains, do not need permission to join or contribute to their network. Whoever wants to be a part of this network can easily view transactions or contribute to the consensus process. This method, based on decentralization and censorship resistance, might create problems related to scaling and governance.
Federated Blockchains
Federated blockchains, on the other hand, are governed by a consortium of organizations instead of a single entity. These blockchains are usually in the case of parties where they collaborate. Also, maintain a small amount of trust between the participants.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain works on a peer-to-peer network where transactions are authenticated and added to the ledger by agreement mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). When the block is added, it becomes difficult to undo. So, the data that has already been recorded will remain unchanged. This way, the system remains secure and reliable to using third parties for verification.
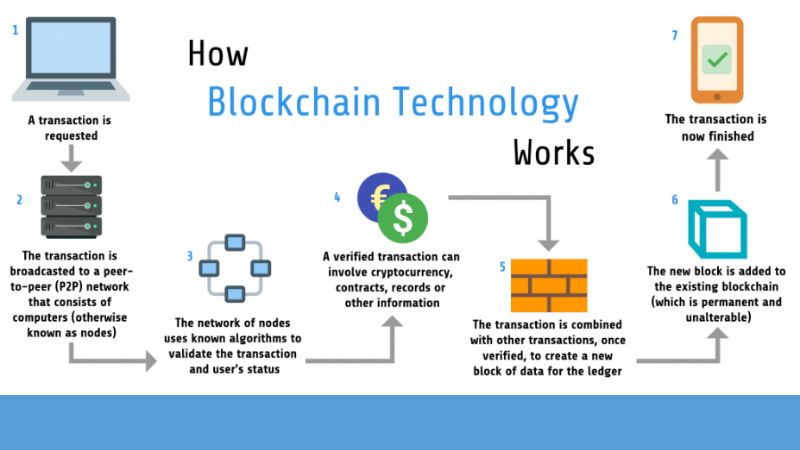
Key Components of Blockchain
Decentralization: As opposed to the traditional centralized systems, Blockchain is based on a decentralized network that eliminates a single point of failure and reduces cyber attack risks.
Cryptographic Hash: Each block in the Blockchain is connected via cryptographic hashes to maintain the vitality of security so that data in terms of transactions cannot be tampered with.
Consensus Mechanisms: There are other consensus mechanisms like proof of work (PoW) and proof of stake (PoS) that validate transactions and secure the integrity of the blockchain network.
Smart Contracts: These smart contracts are self-executing, and thus start executing their terms as soon as the agreement is reached on the contract, streamlining processes and reducing intermediaries.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology finds applications across diverse industries, including:
Finance: Ensuring safe and transparent transactions, implementing fast payments across borders in all directions, and fighting against fraud.
Supply Chain Management: Providing a supply chain with traceability and accountability increases authenticity and ensures quality control.
Healthcare: Health data management improvement, facilitation of medical record sharing with confidentiality, and increasing the possibility of data integration between healthcare providers.
Digital Identity: Providing a decentralized ID verifying system that will keep the personal data information protected from data breaches.
Real Estate: The process of transforming property and assets deals, for the sake of cutting paperwork and precluding fraud.
The Evolution of Blockchain Technology
Early Development
The Blockchain principle was first proposed in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto, as the technology behind Bitcoin, the first-ever coin. Blockchain, however, has been transformed into something far more interesting since then. Developers are busy researching how the technology can facilitate greater efficiency in multiple areas.
Emerging Trends
The advancements in Blockchain technology of recent times entail the increase in decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). It signifies the unique characteristic of Blockchain that it can bring up forms of change in the current system.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Blockchain is providing the vast majority of users with beneficial features like increased security and speed. But, the technology also faces the issues of scalability, regulatory issues, and environmental concerns about the quite intensive energy use for the mining process. The issues arising herein, however, present coinvent soul-searching and growth of the Blockchain space.
Investing in Blockchain Technology
Why Invest in Blockchain?
Blockchain technology promises great development for investors and provides them with room for diversification and building their wealth for sustainable periods. With the adoption continuing to expand across industries, this will lead to crypto-based ventures, and with that investing in the Blockchain and cryptocurrency can give exposure to this innovative technology.
Invest in blockchain by following these tips.
Research: Extenuate the scope of the research by comprehending the basics of the technology, analyzing the market trends, and assessing the possible threats that are linked to Blockchain investments.
Diversification: Reduce your risk by diversifying investments and allocating your assets across different blockchain projects and cryptocurrencies to get the most out of your portfolio.
Stay Informed: Be up-to-date about new developments and regulatory changes as they come up to make better investment decisions.
Future Outlook
Blockchain tech has a promising future, which is driven by the ongoing developments in the field of its application in different sectors. According to governments, businesses, and online shoppers, Blockchain has all the reasons to become the mainstream technology. Blockchain is going to fully accomplish its task of making digital systems decentralized and transparent.



