Maintaining healthy glucose levels is crucial for overall well-being and the prevention of chronic diseases such as diabetes. Glucose, a simple sugar, serves as the primary energy source for our bodies, especially for the brain and muscles during physical activity. Understanding the factors that influence glucose levels and how to manage them effectively can lead to a healthier life. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the importance of glucose, the ideal glucose levels, the factors affecting these levels, and strategies to maintain healthy glucose levels.
Understanding Glucose and Its Importance
What is Glucose?
Glucose is a type of sugar that is found in the bloodstream and is derived from the food we eat. It is a crucial source of energy for the cells in our body. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose and released into the bloodstream, providing immediate energy or being stored for future use.
The Role of Insulin
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that allows cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. It acts as a key, unlocking cells to permit glucose entry, thus regulating blood glucose levels. Without insulin, glucose would remain in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels and potential health complications.
Ideal Glucose Levels
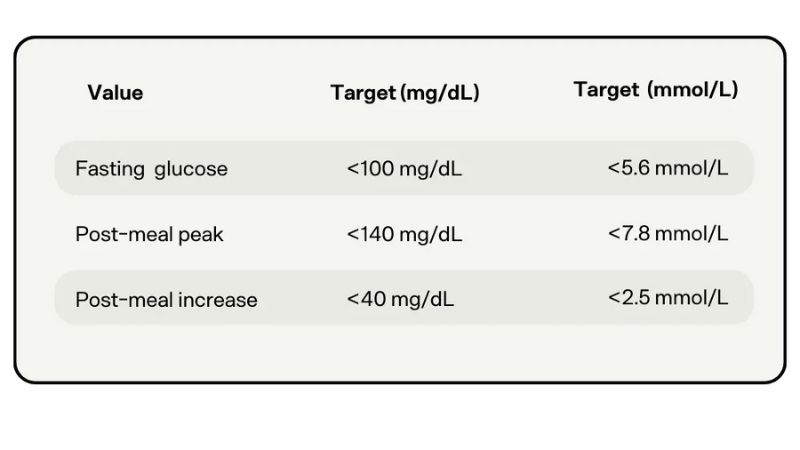
Normal Glucose Levels
Healthy individuals typically maintain blood glucose levels within a narrow range:
- Fasting Blood Glucose: 70-99 mg/dL
- Postprandial (After Meal) Glucose: Less than 140 mg/dL
- HbA1c (Hemoglobin A1c): Below 5.7%
These levels ensure that the body functions optimally and reduces the risk of developing diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Glucose Levels in Diabetic Individuals
For individuals diagnosed with diabetes, the target glucose levels differ slightly:
- Fasting Blood Glucose: 80-130 mg/dL
- Postprandial (After Meal) Glucose: Less than 180 mg/dL
- HbA1c: Below 7%
Maintaining these levels helps manage diabetes effectively and prevent complications such as neuropathy, nephropathy, and cardiovascular diseases.
Factors Affecting Glucose Levels
Diet and Nutrition
The types of food consumed significantly influence blood glucose levels. Foods high in refined sugars and simple carbohydrates can cause rapid spikes in glucose, whereas complex carbohydrates, fiber-rich foods, and proteins help maintain steady glucose levels.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to use glucose more efficiently. Exercise helps lower blood glucose levels and supports weight management, which is crucial for diabetes prevention and management.
Stress and Hormonal Changes
Stress triggers the release of hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase blood glucose levels. Managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and physical activity is essential for maintaining healthy glucose levels.
Sleep Patterns
Poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep can disrupt glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. Ensuring adequate and quality sleep is vital for glucose regulation.
Medications
Certain medications, especially those used in the treatment of diabetes (e.g., insulin, metformin), directly impact blood glucose levels. It is important to follow medical advice and monitor glucose levels regularly when on these medications.
Strategies to Maintain Healthy Glucose Levels
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood glucose levels. Avoiding processed foods and sugary drinks is also beneficial. Incorporating foods with a low glycemic index (GI) can prevent glucose spikes.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can improve glucose metabolism and overall health. Strength training exercises are also beneficial for maintaining muscle mass and enhancing insulin sensitivity.
Stress Management
Adopting stress management techniques such as yoga, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help reduce the impact of stress on blood glucose levels. Regular relaxation practices contribute to overall well-being and glucose control.
Adequate Sleep
Prioritizing sleep hygiene by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants before bedtime can improve sleep quality and glucose regulation.
Regular Monitoring
For individuals with diabetes or at risk of developing diabetes, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential. Using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) can provide valuable insights into how diet, exercise, and other factors affect glucose levels.
Medical Consultation
Regular consultations with healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists and dietitians, can help tailor a personalized plan for managing blood glucose levels. Medication adjustments and lifestyle recommendations from experts ensure effective glucose control.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy glucose levels is a cornerstone of overall health and well-being. By understanding the factors that influence glucose levels and adopting strategies to manage them, individuals can prevent and manage diabetes, enhance their quality of life, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, effective stress management, adequate sleep, and regular monitoring are key components of a holistic approach to glucose regulation.



