The last decade or so has seen the conversation about mental health getting heated and putting the limelight on the aspect of health that is normally ignored, an area as critical as other aspects of well-being. Meanwhile mental knowledge is increased but a prejudice is born that shows the importance of the people just knowing mental health and disorders effects of living with that.
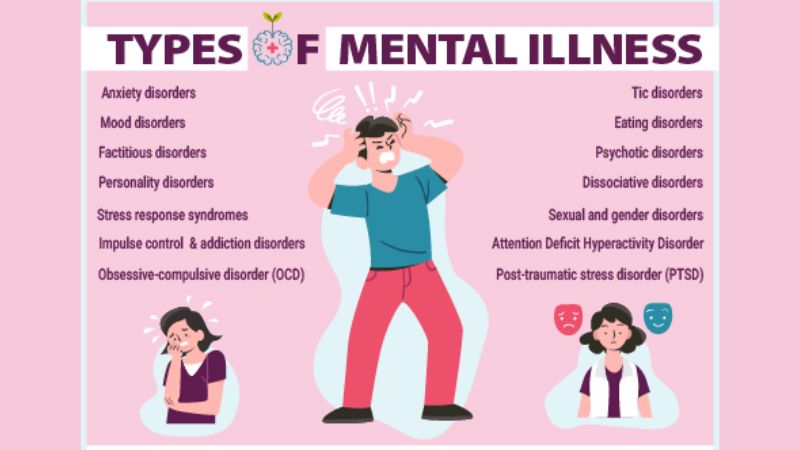
The Significance of Mental Health
Mental health as the concept of emotional, psychological, and social psych well-being is compose on the wide scale of spectrum. It mediates how individuals are perceived, perceived, and behavior through which people become to cope with teen, form relationships, and lead their lives. The importance of mental health in our life is as basic as that of physical wellness in the sense that both of them are needed for one to live a productive and pleasure-filled life.
Common Mental Health and Disorders
Numerous mental health and disorders can manifest in various forms, each presenting its unique set of symptoms and challenges. Some of the most prevalent disorders include:
1. Depression
Depression is a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and disinterest in activities once enjoyed. It can interfere with daily functioning and significantly impact quality of life if left untreated.
2. Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions marked by excessive worry, fear, and apprehension. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Panic Disorder, and Social Anxiety Disorder are among the most common forms of anxiety disorders, each with its distinct features and triggers.
3. Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder involves extreme mood swings that alternate between periods of elevated mood (mania or hypomania) and depression. These mood fluctuations can disrupt sleep patterns, impair judgment, and interfere with relationships and work performance.
4. Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a severe mental illness characterized by distorted thinking, hallucinations, and delusions. It often emerges in early adulthood and can have profound effects on an individual’s perception of reality and ability to function in society.
5. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
PTSD may develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, such as combat, natural disasters, or physical assault. Symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety, leading to significant distress and impairment in daily life.
Addressing Mental Health Challenges
Despite the prevalence of mental health disorders, effective treatments and interventions are available to help individuals manage symptoms and improve their overall well-being. These may include:
Psychotherapy: Talk therapy with a trained therapist can provide valuable support and coping strategies for managing mental health conditions.
Medication: In some cases, medications such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, or mood stabilizers may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques, can promote mental wellness.
Support Networks: Building strong social connections and seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can play a crucial role in recovery and resilience.
Breaking the Stigma
Despite significant strides in mental health advocacy and awareness, stigma and discrimination continue to pose barriers to seeking help and accessing treatment. It is essential to challenge stereotypes, promote empathy and understanding, and foster environments that prioritize mental health and well-being for all individuals.
Conclusion
In the intricate tapestry of human experience, mental health occupies a central thread, influencing every aspect of our lives. By deepening our understanding of mental health and disorders, we can cultivate compassion, support those in need, and work towards a more inclusive and mentally healthy society.



